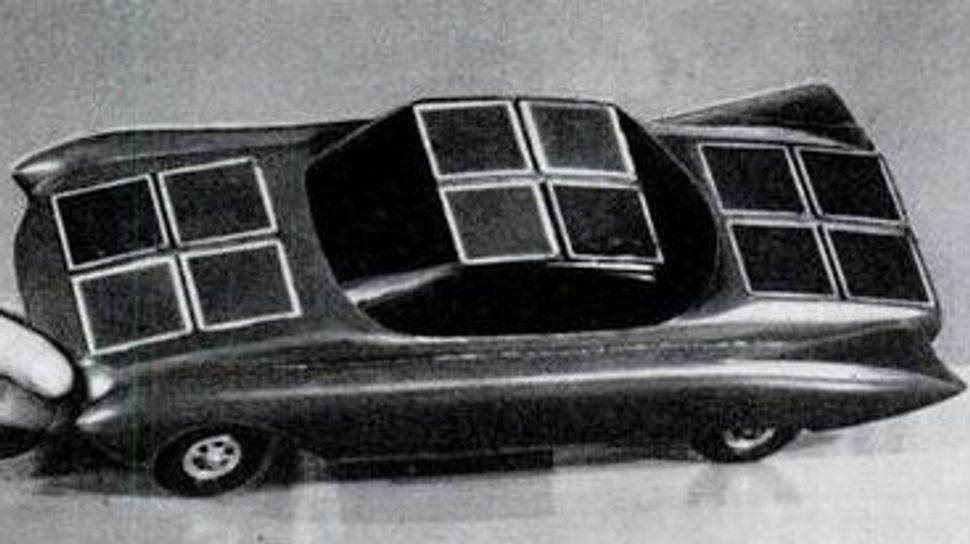
GM Unveils the First Solar-Powered Car

General Motors engineer William G. Cobb introduced the Sunmobile, a miniature automobile powered by sunlight.
What Happened?
The Sunmobile made its debut on August 31, 1955, at General Motors’ Powerama auto show in Chicago, an event showcasing the company’s sprawling empire of diesel engines, machinery, and military equipment. Amid all that petroleum-fueled muscle, William G. Cobb’s miniature solar car offered a glimpse of an entirely different future.
The car itself was only 15 inches long, more toy than transportation. But it harnessed a cutting-edge process called photovoltaics. Twelve photoelectric cells made of selenium captured sunlight and converted it into electricity, powering a small motor. That motor turned a pulley connected to the rear axle, moving the tiny vehicle forward without gasoline, exhaust, or noise.
Visitors marveled at this futuristic curiosity, though few understood its significance. At a time when the automotive industry was wedded to gasoline and America’s highways were filling with tail-finned cruisers, Cobb’s Sunmobile hinted at the possibility of cleaner, renewable energy sources for transportation.
No full-sized solar-powered cars followed immediately. The first drivable model wouldn’t appear until the 1960s, and solar-powered race cars wouldn’t emerge until the late 20th century. Yet Cobb’s Sunmobile was a spark—a reminder that alternative energy could be engineered, even in a world dominated by fossil fuels.
Today, companies around the globe experiment with solar-integrated vehicles, from Dutch startup Lightyear’s solar EVs to California’s Aptera solar-powered cars. While no mass-produced car yet runs fully on sunlight, the Sunmobile of 1955 stands as the playful but profound beginning of solar-powered transportation.
Why It Matters
Cobb’s 15-inch Sunmobile might have seemed like a novelty at the time, but it marked the dawn of solar energy in the automotive imagination. By demonstrating that sunlight could be harnessed to move a machine—even a tiny one—he introduced the idea of a renewable energy future decades before climate change was part of public discourse. Today, as humanity races to move beyond fossil fuels, the Sunmobile reminds us that innovation often starts small, and that even the simplest demonstrations can ignite whole fields of technology.
?
What is photovoltaics, and how does it convert sunlight into usable electricity?
Why was selenium used in the Sunmobile’s solar cells, and what materials are used today?
What challenges have prevented fully solar-powered cars from being mass-produced?
How have modern solar car competitions carried on the legacy of Cobb’s Sunmobile?
In what ways can solar technology complement electric vehicles today?
Dig Deeper
Before the pandemic, Vice visited Lightyear – a startup developing the first solar-powered car – to learn if their project could save the world.
Aptera, a California company, is developing solar-powered cars that may soon enter production, reducing reliance on the electrical grid.
Related

Harnessing the Power of Offshore Wind
Offshore wind energy is one of the fastest-growing renewable energy sources, capable of delivering massive amounts of clean electricity right where people live: along coastlines.

Climate Change and Its Impact on the Future
Climate change is reshaping our planet. From rising temperatures to more extreme weather events, what can we do to mitigate its effects and create a sustainable future?

Powering the Future: Energy and Renewable Solutions
From sunbeams to spinning turbines, renewable energy is shaping our planet’s future. Learn how energy works, where it comes from, and how engineers are helping build a cleaner, brighter tomorrow.
Further Reading
Stay curious!